Home
electronic Wound Quality of Life
eWoundQoL
Quality of life assessment made
easy and quick
What is the eWoundQoL?
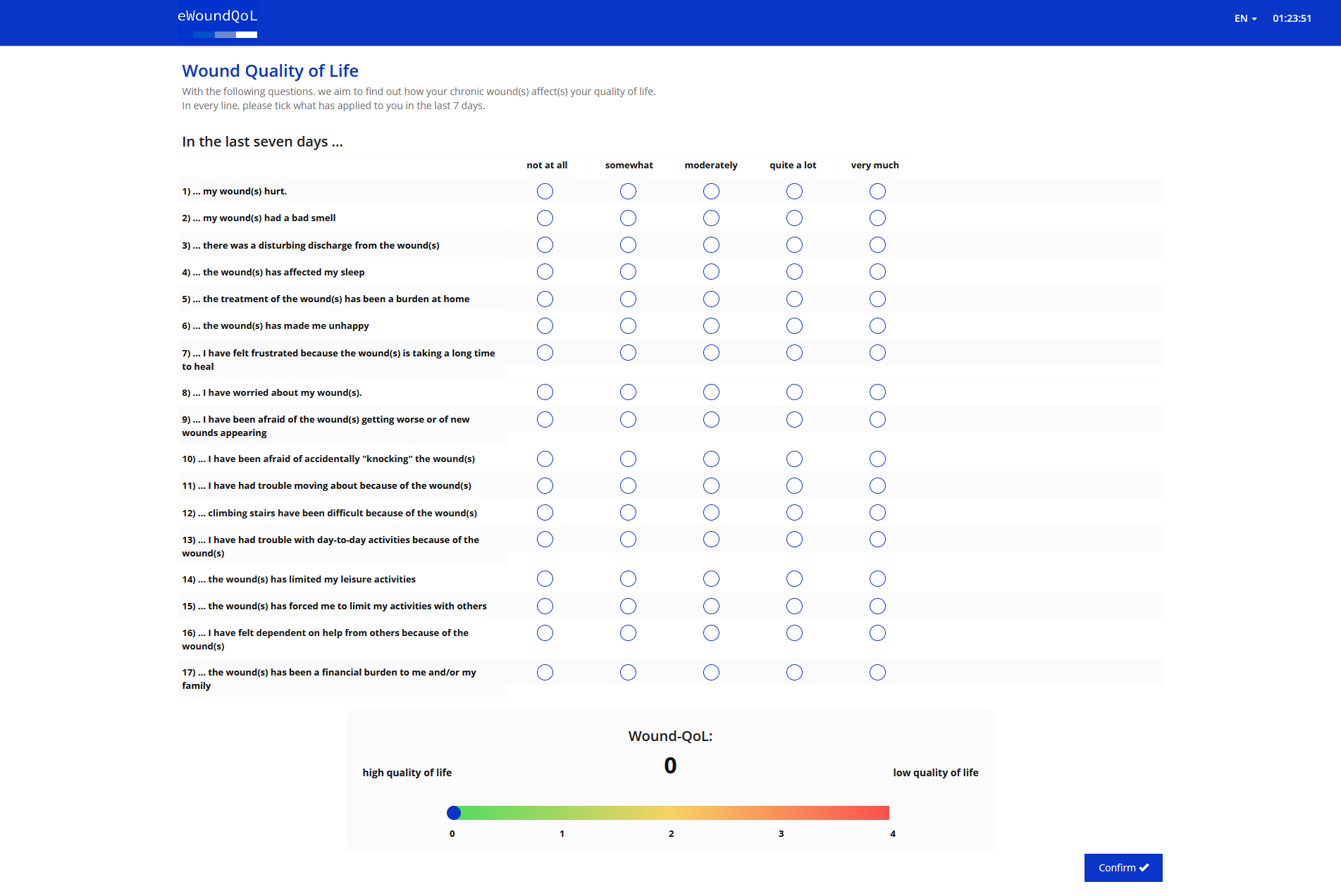
The eWound-QoL measures the disease-specific, health-related quality of life of patients with chronic wounds. It consists of 17 questions covering the quality of life over the last seven days. The eWound-QoL can be used in clinical and observational studies as well as in daily practice.
Validation of questionnaire
paper version: yes digital version: yes
How to use the eWoundQoL
The eWoundQoL consists of 17 questions relating to the three categories of body, psyche and everyday life. These can be answered on a scale from 0 (not at all) to 4 (very much). The eWoundQoL is calculated by taking the mean value of all items or questions. However, at least 13 questions must be answered.
The eWoundQoL is self-explanatory and is completed by patients themselves. If they are not able to complete the questionnaire themselves, they can be assisted. In this case, the support must be documented.
The following versions of the eWoundQoL are available
How it was developed
The Wound-QoL was developed by the Institute for Health Services Research in Dermatology and Nursing at the University Medical Center, Hamburg, Germany. It is derived from three previously existing wound questionnaires, but it is much shorter (one page) and easier to use, making compliance rates higher. Studies have shown the results to be highly reliable. The eWoundQoL is available as a mobile application for Android and iOS devices and as a web-based online calculator.
The impact of chronic wounds
Chronic wounds have a major socioeconomic impact due to their frequency, chronic nature, and societal costs. Patients experience substantial quality of life (QoL) impairments. The most common underlying diseases are chronic venous insufficiency, peripheral arterial occlusive disease, diabetes (diabetic foot ulcers), or pathologic pressure (pressure ulcer).
These conditions and the wounds associated with them can cause severe pain, social isolation, and restricted mobility, thus burdening daily life. Patients who are living with chronic wounds may also experience psychological challenges and conditions such as clinical depression.
As most affected patients are elderly, chronic wounds often coincide with other morbidities common among this age group (e.g., vascular disease, hypertension, obesity), adding further physical and psychological strain. Medical care in the outpatient wound clinic should focus on maintaining or enhancing quality of life. The use of questionnaires for a continuous assessment of quality of life and the resulting interventions to improve the individual's situation are an important cornerstone of guideline-based wound care.
Features
RELIABLE
Studies have shown that the results of the WoundQoL are very reliable.
QUICK
Save time with our online tool. Fill in the questionnaire and your eWoundQoL score will be calculated automatically.
USER-FRIENDLY
The user-friendliness and shortness of the WoundQoL lead to high patient acceptance (> 95% agreement).
MULTILINGUAL
The eWoundQoL is available in 20 different languages. The use of the respective first language reduces language barriers and supports the understanding between physician and patient.
PATIENT-CENTERED
The results of the eWoundQoL provide a patient-oriented analysis of the impact of wounds on quality of life.
ENVIRONMENTALLY FRIENDLY
Take care of the environment and save your patient data on the online platform or as PDF files for yourself and your physicians.
ACCESSIBLE FROM ALL DEVICES
With DermaValue, your eWoundQoL is always just a few clicks away. The application is available for PCs, tablets, smartphones, and other devices.
References
Validity study:
Blome C, Baade K, Debus ES, Price P, Augustin M. The "Wound-QoL": a short questionnaire measuring quality of life in patients with chronic wounds based on three established disease-specific instruments. Wound Repair Regen. 2014 Jul-Aug;22(4):504-14. doi: 10.1111/wrr.12193 . PMID: 24899053 .
Minimal Clinically Important Difference (MCID):
Topp, J., Blome, C., Augustin, M., Mohr, N., Debus, E. S., Diener, H., & Sommer, R. (2021). Determining the Minimal Important Difference for the Wound-QoL Questionnaire. Patient preference and adherence, 15, 1571–1578. https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S315822
Our tools
Our partners





